Part 4: CI/CD and Monitoring with Prometheus & Grafana
Automate your workflow with GitHub Actions and gain deep system insights. Learn to configure CI/CD pipelines for .NET/Angular and build real-time monitoring dashboards with Prometheus and Grafana.
Part 4: CI/CD and Monitoring with Prometheus & Grafana
Introduction
In this part, we will set up automated workflows for testing and deployment, plus add monitoring to watch our system's health. We'll use GitHub Actions for CI/CD and Prometheus & Grafana for monitoring.
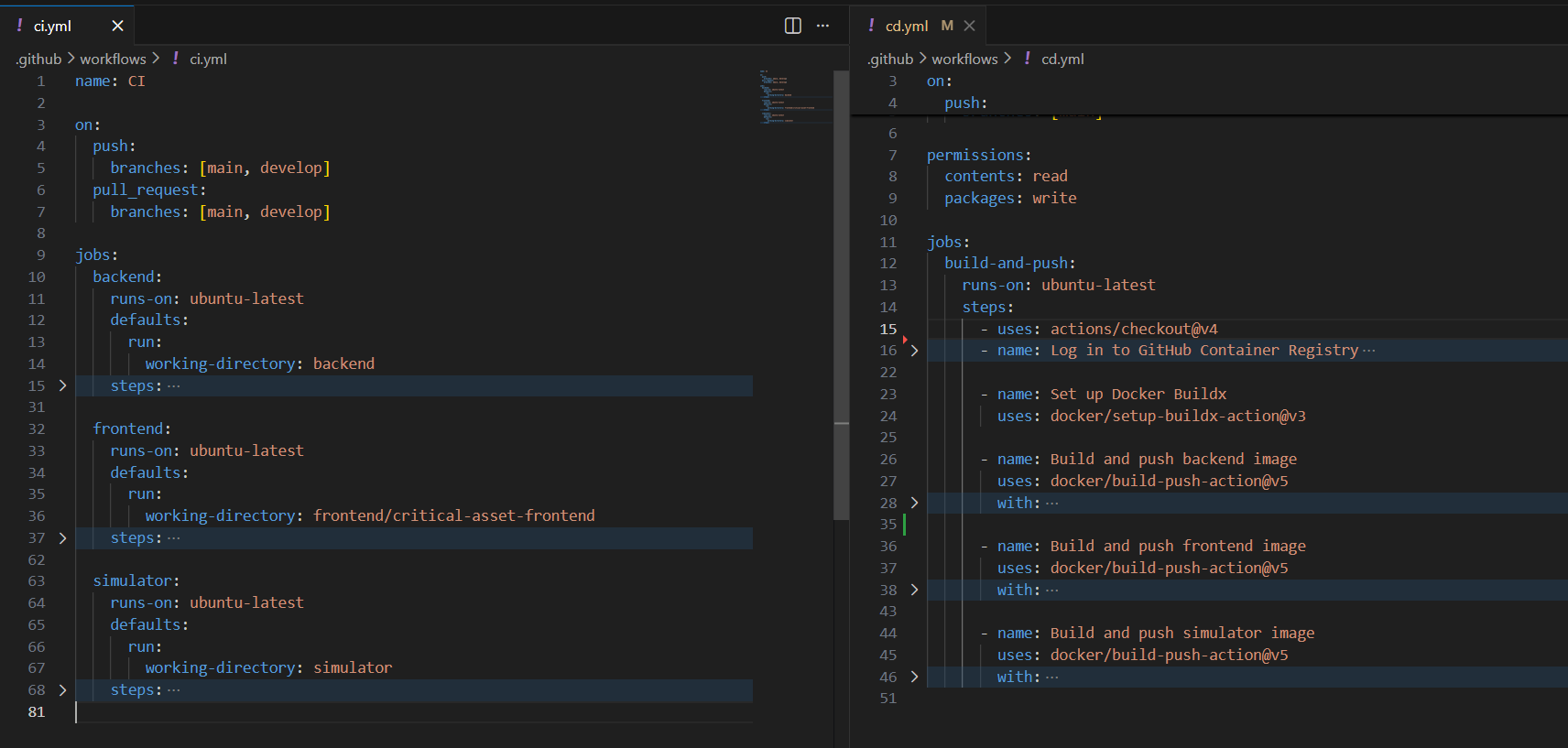
CI Pipeline (Continuous Integration)
The CI pipeline runs automatically when we push code or create a pull request. It checks that everything builds and tests pass before merging.
CI Workflow Structure
Our .github/workflows/ci.yml file has three jobs: backend, frontend, and simulator.
name: CI
on:
push:
branches: [main, develop]
pull_request:
branches: [main, develop]This triggers the pipeline on pushes and pull requests to main and develop branches.
Backend Job
The backend job builds and tests our .NET API:
backend:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
defaults:
run:
working-directory: backend
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Setup .NET
uses: actions/setup-dotnet@v4
with:
dotnet-version: '9.0.x'
- name: Restore
run: dotnet restore
- name: Build
run: dotnet build --no-restore --configuration Release
- name: Test
run: dotnet test --no-build --configuration ReleaseSteps:
- Checkout - Get the code from the repository
- Setup .NET - Install .NET 9.0
- Restore - Download dependencies
- Build - Compile the code
- Test - Run unit tests
Frontend Job
The frontend job checks our Angular application:
frontend:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
defaults:
run:
working-directory: frontend/critical-asset-frontend
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Setup Node.js
uses: actions/setup-node@v4
with:
node-version: '20.x'
- name: Install dependencies
run: npm ci
- name: Lint
run: npm run lint
- name: Build
run: npm run build
- name: Test & Coverage
run: npm run test:coverage
- name: Upload coverage artifact
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
with:
name: frontend-coverage
path: frontend/critical-asset-frontend/coverage/Steps:
- Setup Node.js - Install Node.js 20.x
- Install - Download npm packages
- Lint - Check code style
- Build - Compile the Angular app
- Test - Run tests and generate coverage report
- Upload - Save coverage report as artifact
Simulator Job
Similar to backend, the simulator job builds our telemetry simulator.
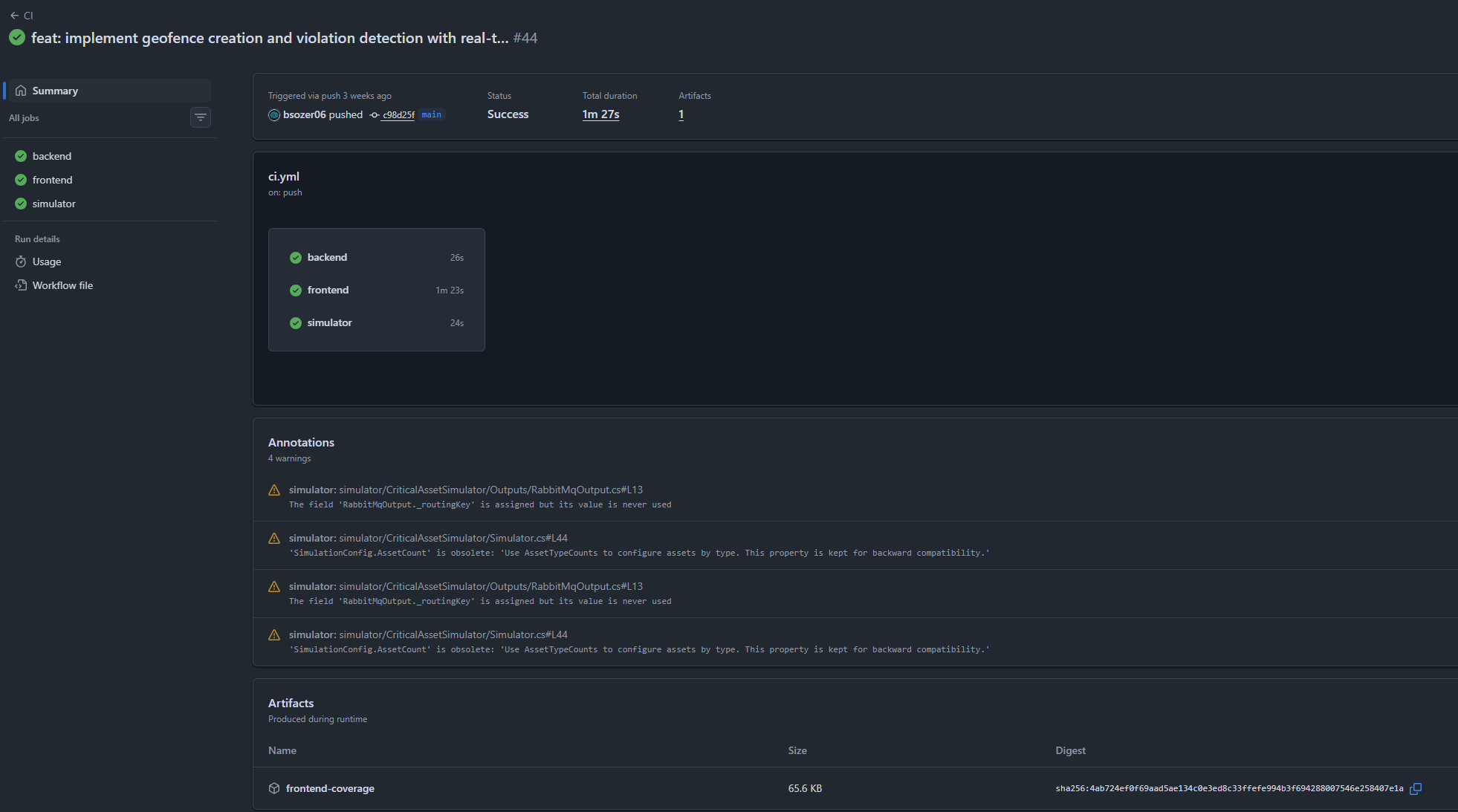
CD Pipeline (Continuous Deployment)
The CD pipeline builds Docker images and pushes them to GitHub Container Registry when code is merged to main.
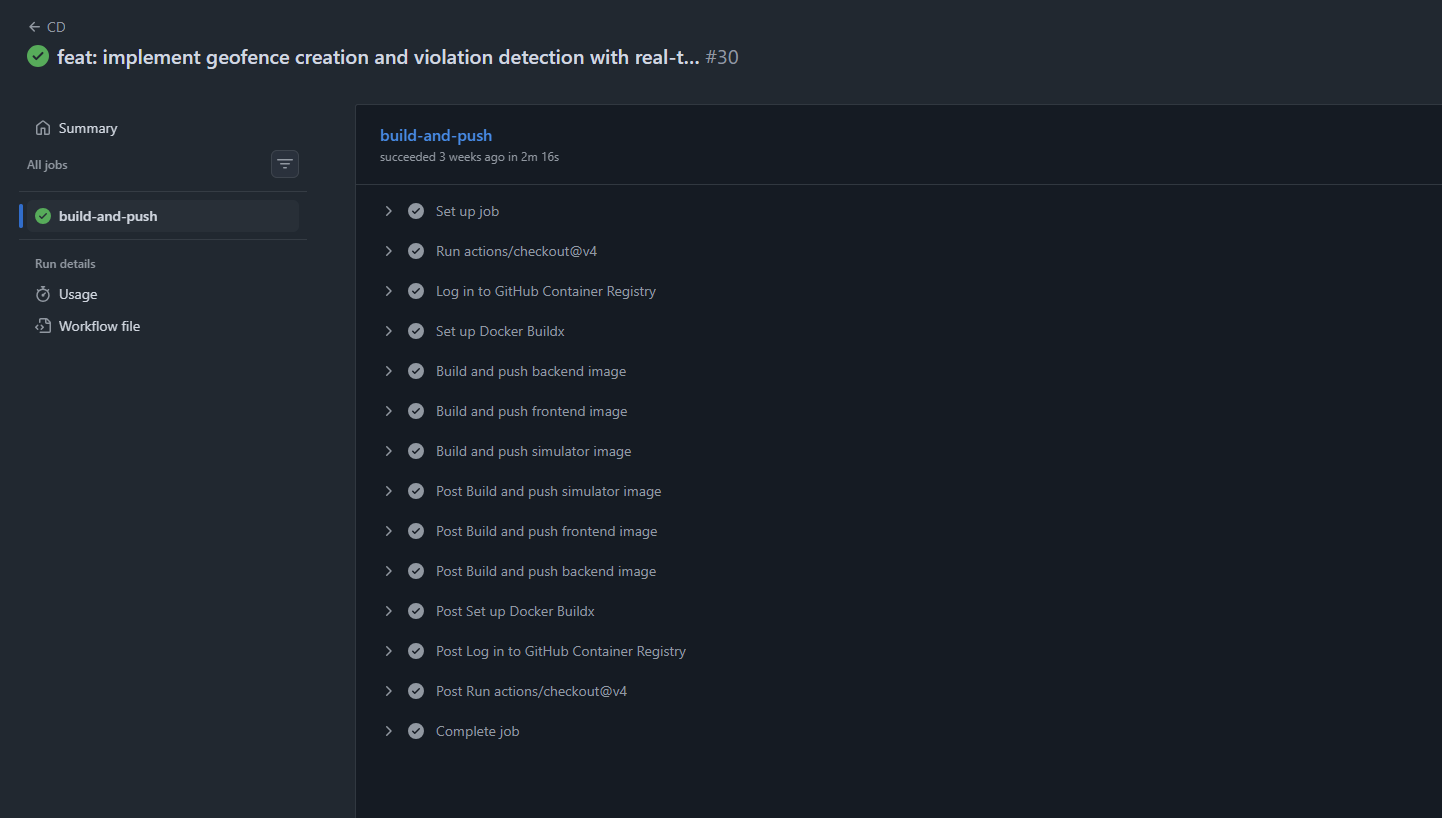
CD Workflow
Our .github/workflows/cd.yml creates and publishes Docker images:
name: CD
on:
push:
branches: [main]
permissions:
contents: read
packages: writeThis only runs on main branch pushes, not on every branch.
Docker Build Steps
- name: Log in to GitHub Container Registry
uses: docker/login-action@v3
with:
registry: ghcr.io
username: ${{ github.actor }}
password: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
- name: Set up Docker Buildx
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v3
- name: Build and push backend image
uses: docker/build-push-action@v5
with:
context: ./backend
file: backend/Api/Dockerfile
push: true
tags: |
ghcr.io/${{ github.repository }}/backend:latest
ghcr.io/${{ github.repository }}/backend:${{ github.sha }}For each service (backend, frontend, simulator):
- Login - Authenticate with container registry
- Build - Create Docker image
- Tag - Add tags (
latestand commit SHA) - Push - Upload to registry
This gives us versioned images we can deploy anywhere.
Monitoring with Prometheus
Prometheus collects metrics from our API to track system performance.
Prometheus Configuration
Our prometheus.yml tells Prometheus where to find metrics:
global:
scrape_interval: 15s
evaluation_interval: 15s
scrape_configs:
- job_name: 'catp-api'
static_configs:
- targets: ['catp-api:80']
metrics_path: /metrics
scrape_interval: 5sSettings:
- scrape_interval: How often to collect metrics (every 5 seconds for our API)
- job_name: Name for this metrics source
- targets: Where to find the API (our Docker container)
- metrics_path: API endpoint that exposes metrics
Application Metrics
We track four key metrics in our application:
// Total messages processed
Counter TelemetryMessagesProcessed = Metrics
.CreateCounter("catp_telemetry_messages_processed_total",
"Total number of telemetry messages processed",
new[] { "asset_type", "status" });
// Processing time
Histogram TelemetryProcessingDuration = Metrics
.CreateHistogram("catp_telemetry_processing_duration_seconds",
"Duration of telemetry message processing",
new[] { "asset_type" });
// Validation errors
Counter ChecksumValidationFailures = Metrics
.CreateCounter("catp_checksum_validation_failures_total",
"Total number of checksum validation failures",
new[] { "asset_id", "asset_type" });
// Active connections
Gauge ActiveSignalRConnections = Metrics
.CreateGauge("catp_signalr_connections_active",
"Current number of active SignalR connections");These metrics help us answer:
- How many messages are we processing?
- How fast are we processing them?
- Are there validation errors?
- How many clients are connected?
Visualization with Grafana
Grafana creates visual dashboards from Prometheus metrics.
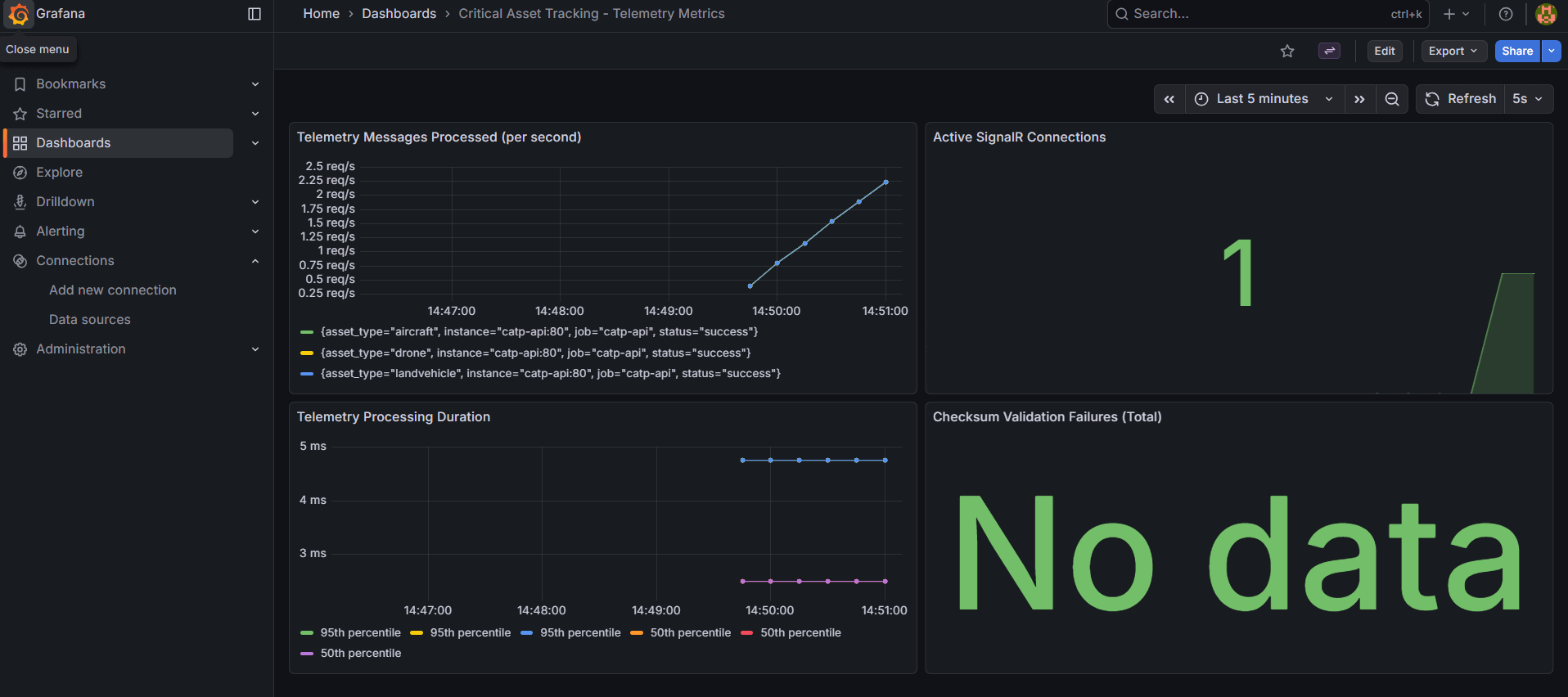
Grafana Setup
The datasources/prometheus.yml connects Grafana to Prometheus:
apiVersion: 1
datasources:
- name: Prometheus
type: prometheus
url: http://catp-prometheus:9090
access: proxy
isDefault: true
editable: trueThis tells Grafana where to get data from.
Dashboard
We have a pre-built dashboard in catp-telemetry.json that shows:
- Messages processed over time
- Processing duration trends
- Checksum validation failures
- Active SignalR connections
- System health metrics
Docker Compose Integration
In our docker-compose.yml, we add Prometheus and Grafana:
prometheus:
image: prom/prometheus:latest
container_name: catp-prometheus
ports:
- "9090:9090"
volumes:
- ./Infrastructure/Monitoring/Metrics/Prometheus/prometheus.yml:/etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml
depends_on:
- api
grafana:
image: grafana/grafana:latest
container_name: catp-grafana
ports:
- "3000:3000"
environment:
GF_SECURITY_ADMIN_PASSWORD: admin
volumes:
- ./Infrastructure/Monitoring/Dashboards/Grafana/provisioning:/etc/grafana/provisioning
- ./Infrastructure/Monitoring/Dashboards/Grafana/dashboards:/var/lib/grafana/dashboards
depends_on:
- prometheusAccessing the Monitoring Stack
After running docker-compose up:
- Grafana Dashboard: http://localhost:3000 (username:
admin, password:admin) - Prometheus UI: http://localhost:9090
- API Metrics Endpoint: http://localhost:5073/metrics
Summary
We now have:
- CI Pipeline - Automatically tests code on every push
- CD Pipeline - Builds and publishes Docker images on merge to main
- Prometheus - Collects metrics from our API every 5 seconds
- Grafana - Shows visual dashboards of system health
This setup helps us:
- Catch bugs early with automated testing
- Deploy consistently with Docker images
- Monitor system performance in real-time
- Debug issues with historical metrics data
The combination of CI/CD and monitoring gives us confidence to deploy frequently while maintaining system reliability.
Prepared by Burhan Sözer
Software & GIS Engineer
