Preventing CORS Errors When Accessing GeoServer from Client-Side Apps
Learn why CORS errors occur when accessing GeoServer (WMS, WFS, WCS) directly from browser-based GIS applications and explore correct, secure server-side solutions including web.xml configuration and reverse proxy architecture.
Preventing CORS Errors When Accessing GeoServer Directly from Client-Side Applications
Introduction
When building modern Web GIS applications (Angular, React, Vue, or plain JavaScript), developers often try to access GeoServer services (WMS, WFS, WCS, WMTS) directly from the browser.
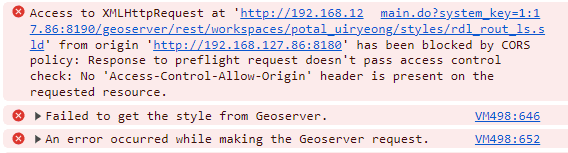
At this point, many encounter the infamous error:
CORS error: No ‘Access-Control-Allow-Origin’ header is present

This article explains why this happens and how to fix it correctly—without unsafe client-side hacks.
What Is CORS (A Quick Look)
CORS (Cross-Origin Resource Sharing) is a critical browser security mechanism.
Its purpose is to prevent malicious JavaScript running on one origin from automatically accessing resources on another origin unless the server explicitly allows it.
An origin is defined as the full combination of:
- Protocol (http / https)
- Domain
- Port
Key Points
- ✅ CORS is enforced by the browser (Chrome, Firefox, Edge).
- ❌ CORS is not enforced by GeoServer itself.
- ❌ CORS cannot be fixed in client-side JavaScript or GIS libraries like OpenLayers or Leaflet.
The Core Problem
If your application runs at:
http://localhost:4200and GeoServer runs at:
http://localhost:8080/geoserverthe browser treats these as two different origins because the ports differ.
As a result, the browser blocks the request unless GeoServer sends the proper CORS headers.
✅ Correct Ways to Fix CORS for GeoServer
There are two correct and production-ready approaches.
Solution 1: Enable CORS in GeoServer web.xml (Simple & Direct)
This approach tells GeoServer to return the requiredAccess-Control-Allow-Origin headers in its HTTP responses.
Step 1: Locate the Configuration File
Navigate to:
...\GeoServer\webapps\geoserver\WEB-INF\web.xmlStep 2: Add or Uncomment the CORS Filter
<filter>
<filter-name>CrossDomainFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.eclipse.jetty.servlets.CrossOriginFilter</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>allowedOrigins</param-name>
<param-value>http://localhost:4200</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>allowedMethods</param-name>
<param-value>GET,POST,PUT,DELETE,HEAD,OPTIONS</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>allowedHeaders</param-name>
<param-value>*</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>Step 3: Map the Filter
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>CrossDomainFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>Step 4: Restart GeoServer
GeoServer must be restarted for changes to take effect.
Solution 2: Reverse Proxy
Instead of exposing GeoServer directly, use a reverse proxy such as Nginx, Apache, or a custom backend API.
Flow
Client -> Reverse Proxy / Backend API -> GeoServerBenefits
- Avoids browser CORS issues
- Improves security
- Enables authentication and logging
- Standard enterprise architecture
Conclusion
- CORS is a browser security feature
- It is not a GeoServer bug
- The fix is always server-side
Trying to fix CORS in JavaScript indicates an architectural issue.